Overcome PC Challenges with Virtual Desktop Solutions
For decades, PCs have been the backbone of business computing. Yet, while their hardware has continuously evolved, their fundamental capabilities have largely remained unchanged. This stagnation has left traditional PCs struggling to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced, digitally transformed business environment. The challenges are clear: heightened data security threats, rising remote work, and the drive for management and cost efficiencies.
In response, virtual desktop solutions offer a powerful alternative. Two primary options stand out: Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS). Both offer distinct advantages and cater to different needs. This article will guide you through the key differences between VDI and DaaS, helping you make an informed decision on the best fit for your organization. Whether you seek robust control with VDI or the flexibility and ease of DaaS, understanding these solutions is the first step towards a more secure, efficient, and adaptive IT strategy.
VDI vs. DaaS: Key Differences
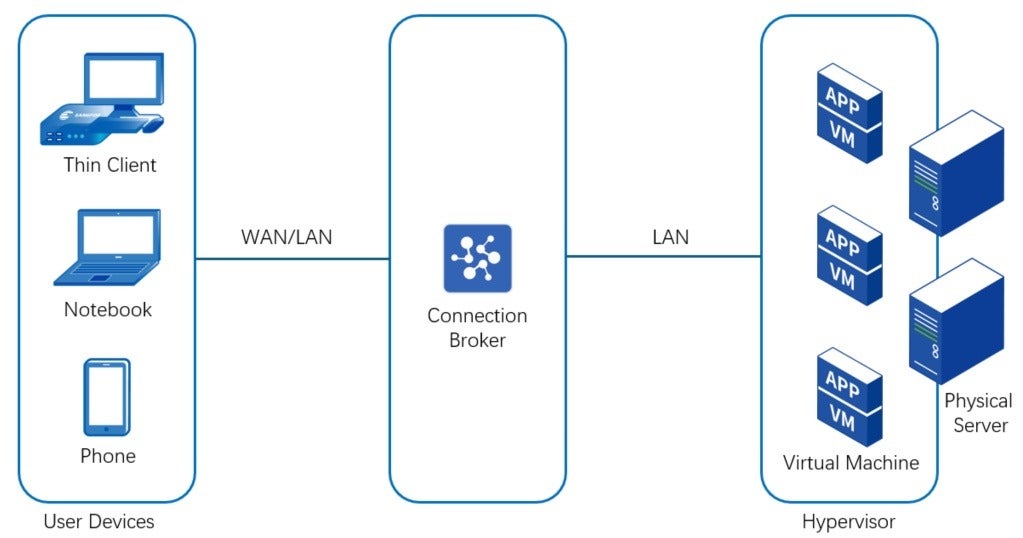
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that allows users to access desktops and applications from any device. Instead of running on your computer, the operating system runs on a virtual machine (VM) in a data center. The virtual desktop image is streamed over a network to your device, whether it’s a PC, thin client, or mobile device. This lets you use your desktop and applications as if they were running locally.
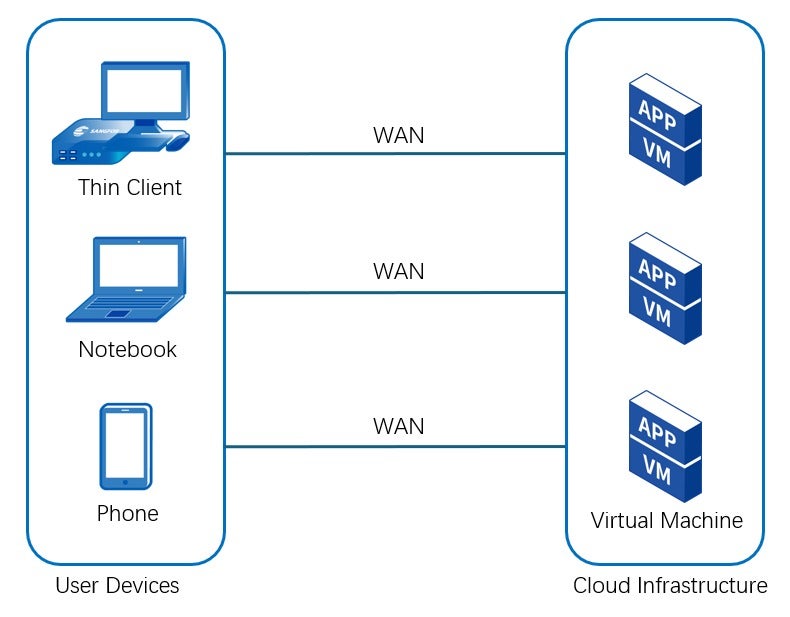
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) is a cloud service that provides virtual desktops and applications on a subscription basis. Unlike VDI, where the infrastructure is owned and managed by your organization, DaaS is hosted in the data center of a cloud service provider (CSP). Users access their virtual desktops and applications from any device via the internet.
1. Architecture and Responsibility
VDI and DaaS share similar architecture and technology. Both use virtualization technology to run VMs and pool hardware resources. Both deliver virtual desktop images over a network to endpoint devices. They also provide unified management and templates to improve IT efficiency.
The main difference lies in infrastructure ownership and management responsibility:
With VDI, customers purchase their own servers and deploy them in their own data centers. The customer, or a managed service provider (MSP), manages the entire infrastructure, including the servers, VMs, policies, and user settings. This setup offers complete control over the environment but requires more management effort.
In contrast, DaaS is hosted in the CSP’s data center. The servers and physical resources (CPU, RAM, storage) are shared with other customers in a multi-tenant setup. This poses greater security and resource availability risks. However, the CSP handles all the maintenance and updates, allowing customers to focus on their core business activities.
Summary
|
Aspect |
VDI |
DaaS |
|---|---|---|
|
Infrastructure Ownership |
Customer |
CSP |
|
Infrastructure O&M Responsibility |
Customer or MSP |
CSP |
|
Infrastructure O&M Effort |
High (or higher cost with MSP) |
Low: CSP handles maintenance and updates |
|
Solution Management |
Customer or MSP |
Customer or CSP |
|
Resource Availability |
Dedicated resources |
Shared resources in a multi-tenant setup |
|
Data Security |
High: Data is stored, processed, and transmitted locally; better data control, visibility, and compliance |
Moderate: Data is stored and processed in CSP infrastructure and transmitted over the internet; less data control, visibility, and compliance |
2. Costs
VDI costs include hardware, software, and services for setup and maintenance, making the initial investment high. This may not be ideal for smaller organizations that do not have enough concurrent users (e.g., under 30) to fully utilize server resources.
On the other hand, DaaS is charged per user on a monthly subscription basis. This results in lower initial costs, making it more accessible for smaller businesses. However, DaaS becomes more expensive as the number of users, server resources, and usage duration increase. VDI, with its perpetual licensing model, is more cost-effective in the long run, especially in scenarios where employees work in shifts, such as call centers, service halls, IT labs, hospitals, and retail environments. Here, VDI’s concurrent user licensing model offers a price advantage.
Summary
|
Aspect |
VDI |
DaaS |
|---|---|---|
|
Cost Model |
Perpetual license or Subscription-based |
Subscription-based |
|
Initial Costs |
High: includes hardware, software, and services |
Low: monthly subscription per user |
|
Suitability for <30 users |
Low |
High |
|
Long-Term Costs |
Low: Cost-effective with more concurrent users |
High: More costly with increased usage and users |
|
Ideal Use Cases |
Call centers, service halls, IT labs, hospitals, retail |
General SME usage |
3. User Experience
Network quality is crucial for the performance of virtual desktop solutions since desktop images are delivered in real time over a network.
A VDI solution operating within a local area network (LAN) offers better fluency and reliability because LAN connections typically provide faster and more stable performance. Except for high-performance use cases like gaming and 3D rendering, the user experience with VDI is similar to using a physical PC for most office tasks.
In contrast, DaaS relies on the internet, making it more prone to latency and downtime, which can disrupt business operations. However, DaaS offers a better user experience for a large, geographically dispersed user base due to the extensive infrastructure and network capabilities of CSPs.
Summary
|
Aspect |
VDI |
DaaS |
|---|---|---|
|
Connection Type |
LAN and Internet (remote users) |
Internet |
|
Performance |
High: Better fluency and reliability with LAN |
Moderate: More prone to latency and downtime with internet |
|
User Experience for General Office Tasks |
Similar to physical PC |
Dependent on internet quality, potentially disrupted |
|
Geographically Dispersed Users |
Less suited |
Better suited due to CSP's extensive infrastructure |
4. Data Security
Data protection is a key factor in choosing virtual desktop solutions. This is because data is not stored or processed on local devices but on backend servers, significantly reducing the risk of data loss and leakage. Moreover, virtual desktop solutions, whether VDI or DaaS, offer a range of security features that prevent users from exporting data to local desktops, storage devices, or the internet.
The following table compares the security features offered by Sangfor VDI and Azure Virtual Desktop (DaaS).
|
Features |
Sangfor VDI |
Azure Virtual Desktop |
|---|---|---|
|
Basic Endpoint Environment Check |
Supported |
Supported Azure Zero-Trust, Charged. |
|
2FA (Identification) |
Supported |
Supported |
|
Zero-Trust Access |
Sangfor aTrust, Charged. |
Azure Zero-Trust, Charged. |
|
Distributed Firewall |
Supported, Free. Based on IP/IP Group/User/VM |
Azure Firewall, Charged. |
|
Screen Watermark |
Supported |
Supported |
|
Anti-screenshot |
Supported |
Supported |
|
Screen Recording for Audit |
Third-party software, Charged. |
Supported, Charged. |
|
Clipboard Control |
Bidirectional Text and all files. |
Bidirectional Text, Images, Rich Text Format, HTML |
|
USB Disk Redirection Control |
Whitelist/Blacklist |
Whitelist |
|
Exported File/Text Audit |
Supported |
Azure Monitor, Charged. |
|
Temporary Policy |
Supported |
N/A |
|
Application Control in VM |
Application Whitelist/Blacklist |
Application Whitelist |
|
Secure VDI (VDI+EDR) |
Sangfor Endpoint Secure + aSEC (EDR works with hypervisor for micro-segmentation) |
Microsoft Defender (Separate component) |
Where VDI and DaaS differ in terms of data security is where the data is stored and how it is accessed.
With a VDI solution deployed on-premises, data is stored within your own infrastructure, ensuring complete control and visibility. Additionally, security policies can be tailored to meet specific requirements, further enhancing data protection.
In contrast, DaaS solutions come with several security challenges and concerns:
- Data is stored in the CSP’s infrastructure, giving customers less visibility and control over their data.
- Data centers may be located in different countries, potentially violating data privacy and localization laws.
- Because virtual desktops are accessed over the internet, there is a greater risk of data exposure.
- Data security depends on the CSP’s measures and practices, which may not always align with a company’s specific needs.
Due to these security concerns, highly data-sensitive organizations, such as those in the finance, government, military, and healthcare sectors, rarely choose DaaS solutions.
Hybrid Solutions
With innovations in business models, the distinction between VDI and DaaS solutions can sometimes blur.
MSPs can deploy servers in a customer’s data center and offer DaaS with maintenance services on a subscription basis. This approach allows customers to enjoy enhanced data security and faster, more reliable network performance. It also eliminates the hassles of management and operation and the need for a large initial investment.
Conversely, organizations can host their own servers with CSPs, or CSPs can provide customers with dedicated server clusters to meet segregation and customization needs, addressing data security, control, and resource availability concerns.
VDI vs. DaaS: Ready to Decide?
Although VDI and DaaS share a similar technical architecture, they cater to different customer needs due to variations in business models and server deployment locations.
On-premises VDI solutions are ideal for organizations that have strict security requirements and need complete control over their data. They are well-suited for businesses with centralized offices or intra-regional telecommuting, where robust and reliable network performance is crucial.
DaaS solutions, on the other hand, offer greater flexibility. They are perfect for customers looking to minimize initial investment costs, achieve rapid deployment and expansion, or provide access to a geographically dispersed workforce.
Explore Sangfor VDI
Sangfor VDI is a one-stop virtual desktop solution that integrates key components—server, hypervisor, connection broker, and thin client—into a single package. Its straightforward architecture, combined with practical management features and an AI operations platform, greatly simplifies operations and maintenance.
Using Sangfor’s advanced virtualization and networking technologies, Sangfor VDI provides efficient and reliable access to virtual desktops, even for remote users, enhancing employee productivity. Additionally, it incorporates Sangfor’s leading security capabilities to ensure robust data protection from internal users and external hackers. It is well-suited for various industries and use cases, including high-performance computing tasks like 3D rendering.
Don't let outdated technology hinder your business. Explore Sangfor VDI for a secure, efficient, and scalable digital workspace.
For more information, visit our Sangfor VDI webpage or contact your local Sangfor office.





