Nearly 1 million Fortinet and SonicWall devices are at risk due to critical vulnerabilities. Is your network protected, or could you be the next target?
Fortinet and SonicWall are prominent names in the cybersecurity industry, trusted by organizations worldwide for their advanced network protection solutions. Fortinet is known for its extensive use in enterprise IT infrastructures, providing robust tools to secure networks and data. Whereas, organizations of all sizes rely on SonicWall for its comprehensive network security technologies, which safeguard digital assets and critical infrastructure.
However, recent security analyses have brought to light alarming vulnerabilities that put nearly 1 million Fortinet & SonicWall devices at significant risk. These vulnerabilities, if exploited, could pave the way for unauthorized access, data breaches, and other potentially devastating cyberattacks.
Reports indicate that these critical security flaws have already been targeted by malicious actors, stressing the urgent need for organizations to take swift action. Promptly addressing these vulnerabilities is crucial to prevent cyber incidents that could otherwise compromise network integrity and the confidentiality of sensitive data. Therefore, IT professionals and decision-makers must stay vigilant and take proactive steps to strengthen their security posture and counter these emerging threats.
Read this article to uncover the latest vulnerabilities affecting Fortinet & SonicWall devices, and discover effective strategies to reduce these risks and strengthen your network security.
FortiOS : Overview & Significance
FortiOS is the core operating system for Fortinet devices, orchestrating various security functions and enabling seamless management across network infrastructures. This powerful OS is integral to the operation of FortiGate firewalls, FortiManager, and other Fortinet products ensuring that enterprises can implement consistent security policies and maintain network protection.
A critical role of FortiOS is to maintain network security through its robust threat detection capabilities, firewall management, and integrated security solutions. It also plays a pivotal role in facilitating secure VPN connections, which are essential for remote work and distributed operations. FortiOS supports a range of security features, including intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and deep packet inspection, thus helping organizations defend against sophisticated cyber threats.
Given its significance, any vulnerability within FortiOS poses serious risks, potentially compromising an organization’s ability to safeguard sensitive data and maintain the integrity of its network infrastructure.
Critical Fortinet Vulnerabilities: CVE-2024-23113 & FortiJump
Fortinet has recently addressed two critical vulnerabilities, each assigned a severity score of 9.8. Reports indicate that attackers have leveraged the Fortinet vulnerabilities to compromise network integrity and gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. The severity of this impact and the scale of potential exploitation made the security community raise alerts.
CVE-2024-23113:
CVE-2024-23113 is a format string vulnerability that affects multiple versions of FortiGate devices (such as FortiOS, FortiProxy, FortiPAM, FortiWeb and FortiSwitchManager). This flaw, which has been exploited, allows attackers to execute arbitrary code by manipulating format string functions within the affected software. Attackers can trigger this Fortinet vulnerability by sending specially crafted input to specific system components, leading to unauthorized code execution. Notably, it requires no user interaction or special privileges to be executed.
CVE-2024-23113 was first disclosed in February 2024. The evaluation of CVE-2024-23113 determined that a successful exploit could severely affect data confidentiality, system integrity, and service availability. Fortinet responded promptly by releasing security patches and advisories to help organizations mitigate the risk. Fortinet strongly advised users of affected FortiGate versions to apply these patches immediately to prevent potential breaches and ensure network security.
CVE-2024-47575 (FortiJump)
CVE-2024-47575, also referred to as “FortiJump,” is the more recent of the two exploited vulnerabilities. CVE-2024-47575 is a critical zero-day vulnerability impacting FortiManager, a tool used for centralized management of Fortinet devices. This flaw allows unauthorized devices to execute arbitrary code or commands within the system.
Exploitation of this Fortinet vulnerability has been ongoing since at least June 2024, and security researchers & FortiManager users had reported attacks linked to an unidentified zero-day vulnerability in the product. This vulnerability was actively exploited by a threat actor group called UNC5820 on June 27, 2024. Attackers successfully exfiltrated configuration data from FortiGate devices managed by compromised FortiManager appliances. The exploitation of this Fortinet vulnerability has also been observed as recently as October 2024, resulting in significant data exfiltration incidents involving FortiGate device configurations.
CVE-2024-47575 stems from a lack of authentication in the ‘fgfmd daemon’, which plays a crucial role in enabling communication between FortiManager and managed Fortinet devices. Due to the importance of this daemon and the significant potential impact of an attack, FortiJump has been rated as "critical," scoring 9.8 out of 10 on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS).
The impact of this Fortinet vulnerability is profound, as it enables attackers to extract configuration data and potentially disrupt managed network operations. Fortinet has acknowledged the active exploitation of this flaw and has recommended that users apply the latest security updates to prevent further breaches. Immediate patching and vigilant monitoring of network traffic are critical steps to mitigate the risks posed by this vulnerability.
SonicWall Devices and Additional Security Threats
SonicWall, another key player in network security, has also faced vulnerabilities that pose significant threats to organizations. These vulnerabilities, if left unaddressed, can lead to unauthorized access and data breaches, impacting the reliability and security of enterprise networks.
CVE-2024-40766:
CVE-2024-40766 is a critical improper access control vulnerability discovered in various SonicWall devices, with a severity score of 9.8. This flaw involves a security weakness that allows attackers to gain unauthorized access by exploiting specific components within the affected devices. Once exploited, this vulnerability could lead to data exfiltration, disruption of services, and potential exposure of sensitive information.
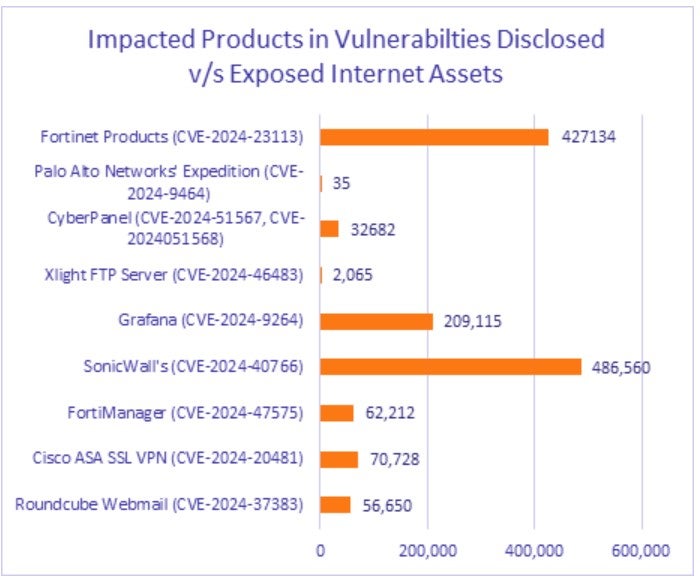
Over 486,000 SonicWall devices were identified as vulnerable to CVE-2024-40766. This vulnerability affects the administrative interface and controls of the SonicOS operating system, which is used to manage SonicWall devices and firewalls. The consequences of a successful exploit are severe, as attackers infiltrate corporate networks, compromise data integrity, and hinder operational continuity.
In response, SonicWall has released a series of updates and security patches to address the issue and strengthen the resilience of their devices against such threats. It is recommended that organizations using SonicWall products apply these updates promptly and implement continuous monitoring to detect and respond to potential exploitation attempts.
Recommendations and Mitigations
By adopting the following mitigation measures, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to cyber threats and maintain a robust defense posture against evolving vulnerabilities:
1. Immediate patching and updates
Applying the latest security patches and updates is crucial for both Fortinet & SonicWall devices to promptly mitigate potential risks and prevent potential exploitation.
Patches & advisories have already been released addressing the Fortinet vulnerabilities, emphasizing the importance of swift action. Neglecting to apply these patches can leave devices exposed to potential attacks, increasing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Administrators are urged to upgrade to secure versions or follow the mitigation steps provided in Fortinet's advisory. One key mitigation measure is to disable ‘fgfm daemon’ access on vulnerable interfaces, though this action prevents FortiManager from detecting FortiGate devices.
Similarly, for SonicWall products, regular patching and stringent access controls are essential to maintaining a strong security posture.
Organizations should closely follow advisories from security agencies and manufacturers to ensure their systems are updated promptly. For instance, agencies such as the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security have issued alerts, urging organizations to patch affected devices without delay to maintain robust security.
2. Network monitoring and threat detection
Continuous network monitoring is essential to identify and respond to suspicious activities. Implementing robust monitoring services such as Managed Detection and Response (MDR) and Network Detection and Response (NDR) can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to detect and mitigate threats in real-time.
3. Access control and authentication enhancements
Limiting device access to authorized personnel is a foundational step in safeguarding networks. Organizations should implement stringent access controls and adopt multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. Restricting device access and ensuring only authenticated users can log in, minimizes the risk of unauthorized breaches.
3. Periodic security audits and assessments
Regular security audits help organizations identify potential vulnerabilities and reinforce their security measures. Conducting comprehensive assessments can pinpoint weaknesses and suggest improvements. Partnering with Managed Security Services ensures that ongoing monitoring and expert guidance are part of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy.
4. Use of EDR tools
Endpoint Detection and Response tools (EDR) play a vital role in safeguarding endpoints against sophisticated attacks. Utilizing EDR tools helps to detect and contain threats before they escalate, ensuring that potential exploits are addressed promptly. These tools provide real-time analysis, enabling swift action to neutralize attacks and minimize damage.
Addressing Critical Vulnerabilities: The Way Ahead
Recent Fortinet vulnerabilities and those in SonicWall devices highlight the severe risks that unpatched systems pose to enterprise security. These vulnerabilities, if left unresolved, open the door to unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential operational disruptions.
Proactive cybersecurity measures are paramount to prevent these threats from escalating. IT professionals must prioritize timely updates, continuous network monitoring, robust access controls, and regular security assessments to maintain a resilient defense against cyberattacks. Employing advanced tools such as EDR, MDR, and NDR further strengthens an organization’s capacity to detect and respond to potential exploits swiftly.
Ultimately, the swift and strategic application of these recommendations ensures that organizations can safeguard their critical infrastructure and sensitive data, staying ahead of evolving cyber threats. IT leaders must act decisively to secure their networks and uphold their commitment to data protection. Addressing these vulnerabilities now will help prevent future cyberattacks and safeguard sensitive data from malicious actors.





