1. Overview of Medusa Ransomware
First observed in 2019, the Medusa ransomware (also known as MedusaLocker) operates as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) business model. It mainly targets the healthcare and educational sectors, as well as enterprises that process high volumes of personal identifiable information (PII). Medusa affiliates typically employ a double extortion tactic that steals the victim’s data before encryption. Victims are threatened with the sale or public release of their data if they do not pay the ransom. Attackers typically gain initial access through brute-force attacks on Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), leaked RDP credentials, or spear-phishing attacks to steal user credentials.
Sangfor noted the urgent advisory issued by the Philippine Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT), cautioning all organizations against Medusa ransomware and other prevalent attacks. For additional details, please refer to the DICT's official advisory: https://dict.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/DICT-Medusa-Advisory.pdf
In response to the recent surge in Medusa ransomware attacks in the Philippines, Sangfor has collected an extensive list of Indicators of Compromises (IOCs) and Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) related to Medusa, seen in the wild by our Neural-X Threat Intelligence platform.
Sangfor Neural-X gathers threat intelligence data from multiple external sources and correlates with anonymous data seen in the wild to obtain the latest IOC and TTP information to help you stay secure.
Disclaimer: Threat actors commonly use different TTPs, IOCs, and tools to bypass and infiltrate different network setups. They may continually adapt by using other or newer tools for greater effectiveness in executing their attacks. Thus, the IOCs and TTPs provided in this article may not fully represent all IOCs and TTPs used in Medusa ransomware attacks. We recommend subscribing to Sangfor Neural-X Threat Intelligence feeds to fully access the latest threat intelligence data and improve effectiveness in detecting and preventing other malicious activities and tools.
Contact your nearest Sangfor office to explore suitable solutions and services that best meet your needs in staying resilient against Medusa Ransomware attacks.
2. Analysis of Medusa Ransomware
2.1 Description of Medusa Ransomware
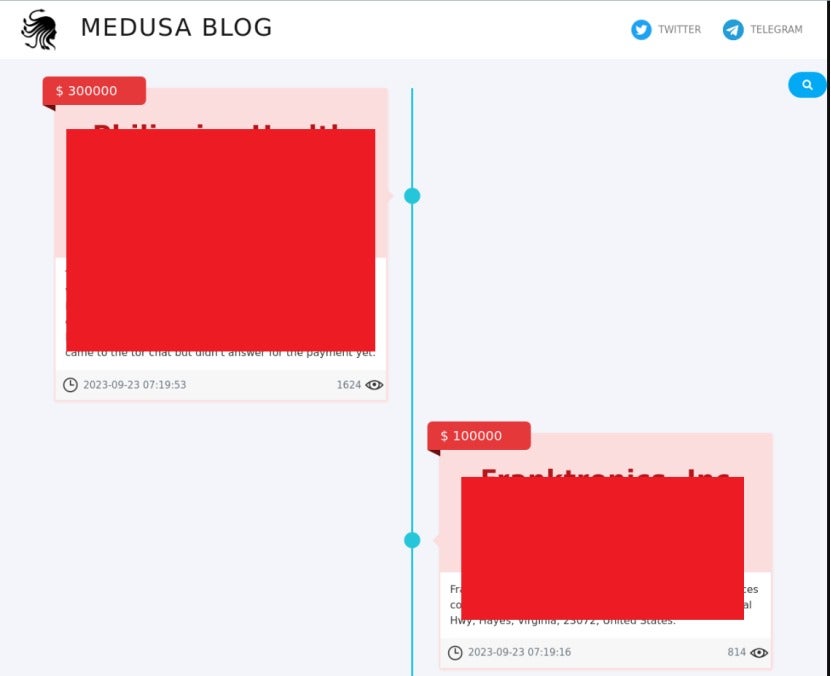
The Medusa ransomware group has escalated its activities since March 2023, increasingly targeting global enterprises. The group launched the "Medusa Blog" to leak data exfiltrated from victims who refused to pay. Information on several victims has been published on this blog, as shown in the figure below.
Our threat intelligence data reveals that Medusa commonly exploited the following vulnerabilities, among others:
- CVE-2022-2294: Heap buffer overflow vulnerability in WebRTC
- CVE-2022-2295: Type confusion vulnerability in Google Chrome V8
- CVE-2022-21999: Windows Print Spooler elevation of privilege vulnerability
- CVE-2018-13379: FortiOS path traversal vulnerability
To mitigate these vulnerabilities, it is critical to keep all software up to date, as adversaries continually adapt their TTPs to maximize the success rate of attacks.
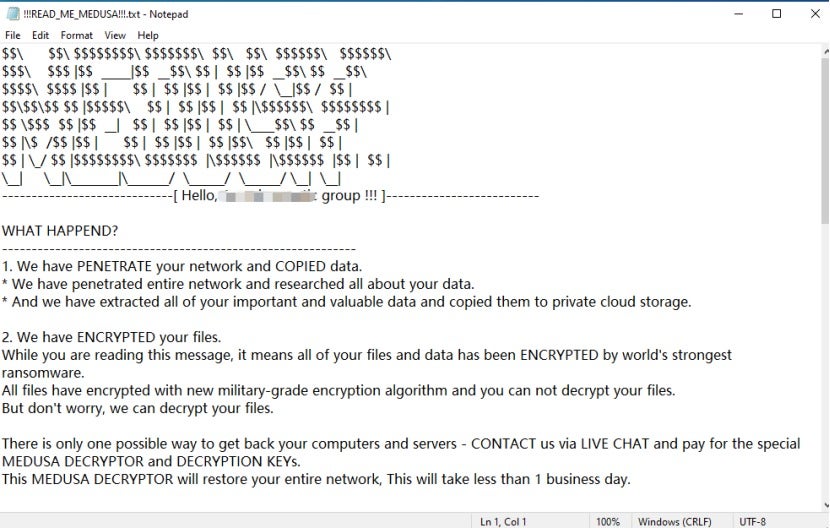
After the ransomware encryption file is executed, a ransom note file is released. Encrypted files are appended with the ". MEDUSA" extension. The ransom note contains the attacker’s contact details in the form of a Tor browser link, payment method, and the ransom amount for decryption. The ransom note file is usually named "!! READ_ME_MEDUSA!!!. txt".
Below is a sample of a Medusa ransom note in a text file format:
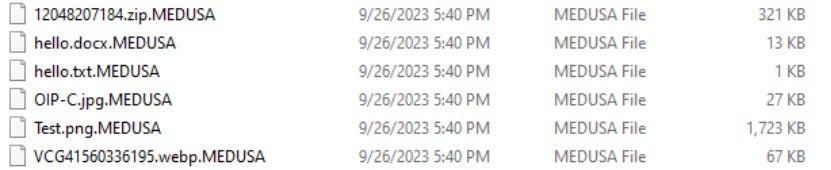
Below is a sample of files encrypted by Medusa ransomware:
2.2 MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Below is a list of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTP) associated with Medusa Ransomware, mapped against the MITRE ATT&CK framework. It serves as a guideline for identifying malicious or suspicious events related to Medusa ransomware. Readers are advised to use this as a guide and not as a strict checklist to identify Medusa TTPs, which may differ between attacks.
| Tactics | Techniques | Sub-Techniques | Description/Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA0001 Initial Access |
|
T1078.003 Local Accounts | Through brute forcing or compromised credentials of legitimate RDP accounts |
| T1566 Phishing | T1566.001 Spear phishing Attachment | Gain initial access via phishing email attachments | |
| T1133 External Remote Services | N/A | Access the victim's network through an RDP service | |
| TA0002 Execution | T1059 Command and Scripting Interpreter | T1059.003 Windows Command Shell | Use a series of Windows commands such as bcdedit.exe and vssadmin |
| T1047 Windows Management Instrumentation | N/A | Use Windows Management Instrumentation Command line (WMIC) to delete shadow copies | |
| TA0005 Defense Evasion | T1562 Impair Defenses | T1562.001 Disable or Modify Tools | Terminate services or processes related to anti-virus/security tools |
| T1562.009 Safe Mode Boot | Abuse safe mode to evade endpoint detection | ||
| TA0006 Credential Access | T1110 Brute Force | T1110.002 Password Cracking | Brute force the password of the local RDP account |
| TA0007 Discovery | T1057 Processes Discovery | N/A | Enumerates all running processes in the current system environment |
| T1083 File and Directory Discovery | N/A | Queries the specified file, folder, and file extension | |
| T1135 Network Share Discovery | N/A | Enumerate network shares | |
| TA008 Lateral Movement | T1021 Remote Services | T1021.001 Remote Desktop Protocol | Use RDP for lateral movement |
| T1021 Remote Services | T1021.002 SMB/Windows Admin Shares | Lateral movement via SMB | |
| TA0011 Command and Control | T1105 Ingress Tool Transfer | N/A | Use certutil to download malicious files |
| TA0040 Impact | T1490 Inhibit System Recovery | N/A | Delete shadow copies and disable the Windows System Recovery feature |
| T1489 Service Stop | N/A | Terminate processes and services related to database servers, mail servers, and backups | |
| T1486 Data Encrypted for Impact | N/A | Use the AES-256 algorithm to encrypt files on the computer |
2.3 Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
2.3.1 File Hashes
Make sure that your endpoint security solution and other security tools are configured to detect, identify, and alert you about malicious files commonly associated with Medusa ransomware. The file hashes of these files are as follows:
| MD5 | 00A0A0A0A59C0F6579999B8B1523 |
| MD5 | 08278e867322735de9e75f59b539426e |
| MD5 | 120e36c2428a4bfe9f37b977f698fa39 |
| MD5 | 217b5b689dca5aa0026401bffc8d3079 |
| MD5 | 3030943c7e5f2c7b710c416f7d979c25 |
| MD5 | 30e71d452761fbe75d9c8648b61249c3 |
| MD5 | 312e41aa5901f6e00811de343627d418 |
| MD5 | 38b1cdb61aff9b5096cc971cbb3159e0 |
| MD5 | 412568f078ec521bdba6ae14b9f36823 |
| MD5 | 4293f5b9957dc9e61247e6e1149e4c0f |
| MD5 | 4536297338323c00783fdceabf8d36bf |
| MD5 | 47d222dd2ac5741433451c8acaac75bd |
| MD5 | 4984d9af56c39a161b627e019ed2604d |
| MD5 | 5b9ee071922cd3a060a4979a403e0f |
| MD5 | 6701070c21d3c6487c3e6291f2f0f1c9 |
| MD5 | 7405efcdd3e931cde430317df1c00131 |
| MD5 | 7b9dbd1a611dc4d378607e5f50b23654 |
| MD5 | 7ecc2ed7db7bbb6dc794f29feb477c8c |
| MD5 | 82143033173cbeee7f559002fb8ab8c5 |
| MD5 | 84b88ac81e4872ff3bf15c72f431d101 |
| MD5 | 858ffbe870a7454c4a59f889d8d49169 |
| MD5 | 8cd11f34d817a99e4972641caf07951e |
| MD5 | 9353a3fa46ce13ea133cfab51c8cbd7a |
| MD5 | 99a1f6e096dc79b1bc1adbefaa0cd9c5 |
| MD5 | acb0fde71fa3d57261e8eac9c3da88ab |
| MD5 | ad182ac22ee9e8075a324fcee2038108 |
| MD5 | d02e837ecc8d57f66d6911b7286c9e71 |
| MD5 | d82b27fdcc3a63f2ab0c46c5a3caef0a |
| MD5 | d8550fb34f73ccc47b02c51b138b11dd |
2.3.2 Command and Control (C2) IP Addresses
Adversaries often use different IP addresses for command and control (C2) to evade detection by security controls. Below is a list of IP addresses observed by our threat intelligence initiating Medusa C2 connections.
Disclaimer: The list below does not represent an up-to-date and exhaustive list after the time of this article’s publication. Threat actors regularly update their TTPs and IP addresses to improve the effectiveness of attacks. All data shared in this document should be treated as a guideline. Apply defense-in-depth using multiple layers of cyber security controls to ensure higher threat detection and protection capability.
195.123.246.138
138.124.186.221
159.223.0.9
45.146.164.141
185.220.101.35
185.220.100.249
50.80.219.149
185.220.101.146
185.220.101.252
179.60.150.97
84.38.189.52
94.232.43.63
108.11.30.103
194.61.55.94
198.50.233.202
40.92.90.105
188.68.216.23
87.251.75.71
196.240.57.20
198.0.198.5
194.5.220.122
194.5.250.124
194.5.220.124
104.210.72.161
3. Recommendations to Prevent Medusa Ransomware
Sangfor leverages the experience of its Cyber Guardian Incident Response (IR) team in managing ransomware attacks and other cyber threats. We offer the following recommendations in relation to people, processes, and technology to keep you secure against Medusa and other ransomware variants.
Process
- Conduct technical security assessments, such as vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT), to identify all security loopholes and vulnerabilities. Ensure unused remote access ports such as TCP/3389 (RDP) and the ports of other remote access applications (e.g., TeamViewer, AnyDesk, and VPN) are disabled from public Internet access or restricted only to selected users and/or IP addresses.
- Register for Sangfor’s Ransomware Exposure Assessment service to identify commonly abused security gaps in ransomware attacks. This service uses Sangfor Endpoint Secure to automate the assessment and generate a report on your ransomware exposure level and risks. Security experts from the Cyber Guardian services team apply their experience in offense and defense to identify critical findings and prioritize remediation efforts.
- Only provision remote access applications (e.g., TeamViewer, AnyDesk, and VPN) that support two-factor or multi-factor authentication (i.e., 2FA or MFA). Consider the Sangfor Network Secure next-generation firewall if your current VPN does not support 2FA/MFA.
- Configure all admin-privileged or remote access accounts with long and strong passwords. Enhance password policy with best practices, such as passwords with a minimum of twelve (12) characters and a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Periodically change the password with a relatively different structure and pattern to prevent brute force attempts.
- Errors and alerts in security controls must be monitored at all times to detect anomalies (e.g., disabled antivirus, suspicious remote connection, malicious files or command execution) and responded to with industry best practices in a timely manner to stop any attack attempts. Consider a Managed Detection and Response (MDR) service, such as Sangfor Cyber Guardian MDR, to manage security threats on a 24x7 basis with industry best practices applied in responding to all security threats by security experts with experienced backgrounds.
- Ensure servers, firmware, and software are updated to the latest versions on a timely basis.
- Carefully manage or restrict the use of personal devices on the corporate network. This prevents threats on personal devices from spreading to the company’s IT assets or network.
Technology
1. Ensure endpoint security or antivirus (AV) software is installed and always updated with the latest virus signatures. Consider endpoint security with anti-ransomware capabilities, such as Sangfor Endpoint Secure, with features such as (but not limited to):
a. Ransomware Honeypot: Uses decoy files to detect ransomware encryption to kill the encryption process in real time.
b. Micro-segmentation: Blocks ports and host access to prevent the propagation of attacks or the spread of infection.
c. Fileless protection: Stops PowerShell command execution without authorization.
d. RDP brute force attack protection: Limits, detects, and stops multiple password-guessing attempts.
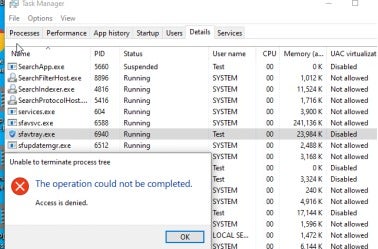
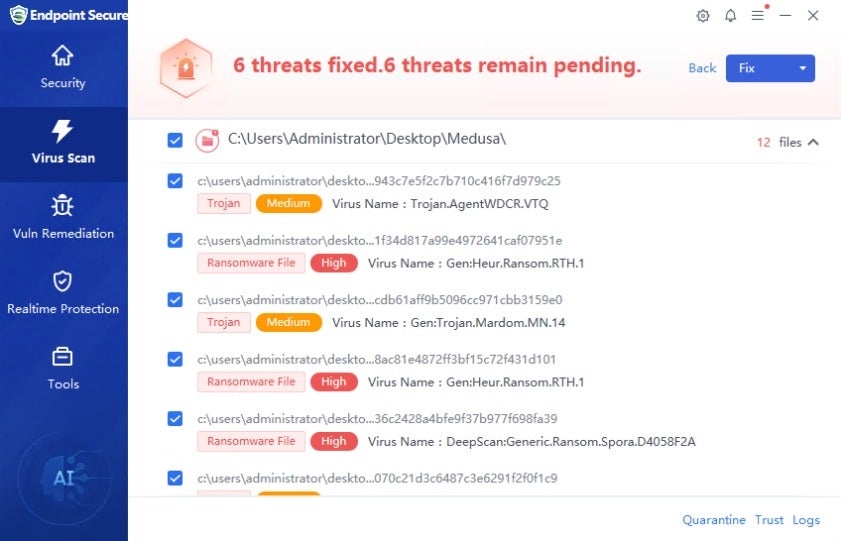
e. Additionally, Sangfor Endpoint Secure could not be easily disabled by hackers to bypass and run malicious files, as shown below;
f. Perform a full organization-wide antivirus scan to ensure all malicious files noted in this investigation are identified and removed.
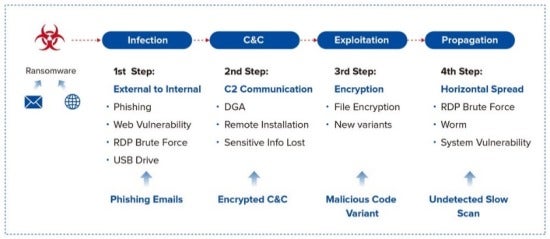
2. Consider the Sangfor Anti-Ransomware solution if you currently do not have technology controls capable of managing ransomware attacks in all stages of the ransomware kill chain, as shown below:
3. Subscribe to Sangfor Neural-X Threat Intelligence for the latest IOCs and TTPs observed in the wild and various other party-party threat intelligence sources. Alternatively, verify any suspicious data through Sangfor’s threat intelligence webpage: https://sec.sangfor.com.cn/index/abroad?lang=EN-US
People
- Educate and remind staff that all remote access applications should be closed or disabled when not in use. Set an auto-logoff control to terminate any remote connections that have been inactive for over 5 minutes.
- Conduct periodic staff awareness training or notification on the latest social engineering techniques used by Medusa and other threat actors. Conduct assessments or simulated social engineering drills to verify the staff’s level of understanding.
- Hire security experts with the right offensive and defensive experience to continuously monitor and respond to threats using mature and proven response processes in accordance with the company’s risk tolerance and risk management strategies.
4. Sangfor Solutions
4.1 Sangfor Endpoint Secure
Sangfor Endpoint Secure is a comprehensive endpoint security solution designed to protect endpoint devices against malicious threats, including ransomware like Medusa. It uses a multi-layered detection and response approach that includes static and dynamic behavioral detection engines and an AI-enabled detection engine, which is trained with thousands of real attack samples seen across our customer’s environments. It achieves over 99.83% detection accuracy and has defended 12 million endpoint devices. Sangfor Endpoint Secure is also the world’s first endpoint security solution integrating a ransomware honeypot. By setting up decoy files, it instantly kills the ransomware encryption process once detected and offers One-Click Kill to remove the ransomware from all infected devices.
4.2 Sangfor Network Secure
Sangfor Network Secure (formerly Sangfor NGAF) is a converged next-generation firewall effective against advanced threats like ransomware, advanced persistent threats (APTs), web application attacks, and IoT exploits. It integrates multiple security features, including intrusion prevention system (IPS), application control, cloud deception, and web application firewall (WAF), and uses AI-enabled Sangfor Engine Zero and Neural-X for detecting emerging and 0-day threats. When integrated with Sangfor Endpoint Secure, both systems exchange threat intelligence and correlate events for improved detection of stealthy behavior like C2 communication. The single dashboard offers a comprehensive threat overview and enables administrators to quickly quarantine malicious processes, making it a robust tool for early-phase ransomware mitigation.
4.3 Sangfor Cyber Command
Sangfor Cyber Command is a Network Detection and Response (NDR) platform that provides proactive defense against cyber threats like ransomware. It continuously monitors and analyzes network traffic in real time to detect threats that have breached the network. Utilizing AI-driven analytics and real-time threat intelligence feeds, it detects 95% of network anomalies, including signs of ransomware activity. Cyber Command also provides insights into vulnerabilities, such as weak passwords and uninstalled patches, enabling security teams to mitigate risks before they can be exploited. The platform integrates seamlessly with Sangfor and third-party security products to provide automated incident response. Analysts get enhanced visibility and tools for in-depth investigation, allowing for prompt remediation and bolstering overall security posture.
4.4 Sangfor Anti-Ransomware Solution
The Sangfor Anti-Ransomware Solution takes a comprehensive approach to ransomware protection by breaking every step of the "Ransomware Kill Chain," a specific sequence of events that includes infection, C2 communication, exploitation, and lateral movement. Individual security products like network firewalls and antivirus often fall short due to gaps between their spheres of influence, as demonstrated by the Medusa ransomware that infected thousands of systems across the Philippines in a matter of days. Sangfor’s solution fills these gaps, providing a more holistic and effective defense strategy against ransomware attacks.
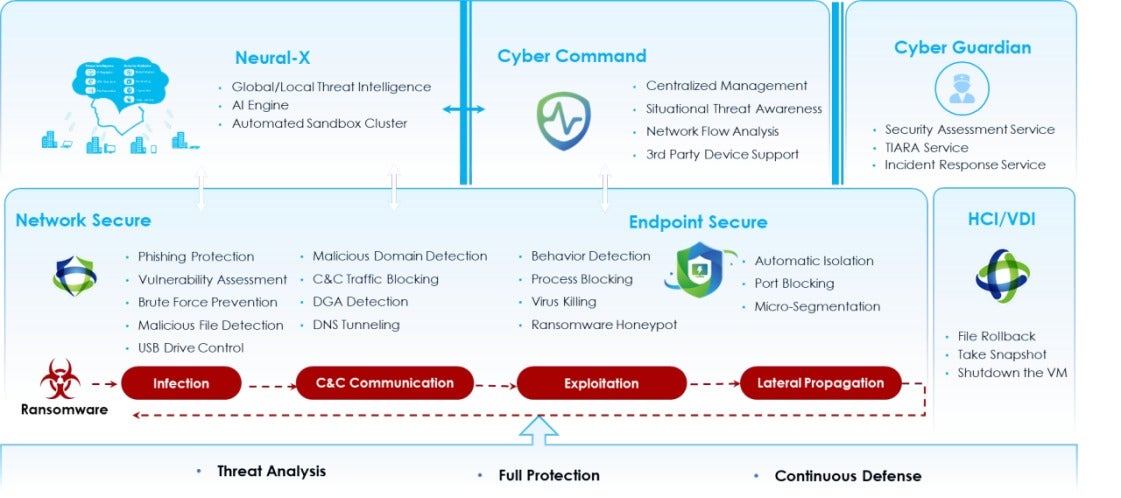
4.5 Sangfor Cyber Guardian MDR Service
The Cyber Guardian MDR service provides organizations that have limited security capabilities with essential threat detection and response services. The service uses a variety of Sangfor security technologies to continuously monitor your network to detect threats. Security experts are on duty 24x7 to analyze security alerts, rapidly respond to threats, and investigate incidents to improve your security posture.
Against the backdrop of a surge in ransomware activities, Sangfor will be introducing a new service component in the Cyber Guardian MDR service that is designed to evaluate our customers’ IT assets, identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that are commonly exploited by ransomware, and provide necessary response actions and recommendations to prevent the possibility of a ransomware attack. This evaluation will be provided using a combination of Sangfor Endpoint Secure and other tools.
This evaluation service will be available as part of the Sangfor Cyber Guardian MDR service by the end of October 2023, so do register your interest with your local Sangfor sales representatives.





