What is a DDoS Attack?
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack is a malicious effort to disrupt normal traffic to a server, web service, or network by overwhelming it or its surrounding infrastructure with a flood of Internet traffic. This is achieved using a network of compromised devices called a botnet as the source of attack traffic. DDoS attacks can result in service unavailability, data breach, reputational damage, and financial loss.

How DDoS Attacks Work
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack operates by overwhelming a target, which could be a website, online service, or network system, with a flood of internet traffic. This is orchestrated through a network of compromised devices known as a botnet. The creation of this botnet begins when attackers infect various internet-connected devices with malware. This can include not just traditional computers and mobile phones but also an expanding array of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and even virtual machines (VM).
These devices are typically compromised through untargeted attacks. Common tactics include phishing emails, malicious downloads, and worms, which spread malware indiscriminately across a wide range of devices.
Once a device is infected, the malware establishes a connection to the attacker’s command and control (C2) server. This connection allows the attacker to remotely control the compromised device, now termed a ‘bot’ or ‘zombie.’ As more devices are infected and connected to the C2 server, a botnet—a network of these bots—is formed.
When the attacker decides to launch a DDoS attack, they send instructions to the botnet. Each bot in the network then sends requests to the target’s IP address. The sheer number of requests, coming simultaneously from thousands or even millions of bots, overwhelms the target’s resources, leading to a denial of service. This attack prevents legitimate users from accessing the service or network, causing significant disruption and potential damage.
DoS Attack vs. DDoS Attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack involves a single source attempting to overwhelm a target service or network with traffic. The scale of a DoS attack is constrained by the resources of the single machine. Typically, this could range from a few gigabits per second (Gbps) to, in rare cases, tens of Gbps, depending on the attacker’s resources.
In contrast, a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack leverages thousands or even millions of compromised devices in a botnet to launch a coordinated attack on the target. These attacks often exceed 100 Gbps and can even reach one terabit per second (Tbps). The scale of a DDoS attack can be so vast that it can overwhelm even well-resourced and protected targets, making it a significantly more formidable and disruptive type of attack.
Types of DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial of Service attacks come in various forms, but they all share the same goal: to render an online service or network unavailable.
To illustrate how different DDoS attacks work, let’s consider an analogy where a city represents a website. Here’s how the elements of the city correspond to parts of the website:
- The entire city: The website in its entirety, encompassing all its web pages, applications, and services.
- Roads: Network pathways that facilitate access to different sections of the website.
- Traffic: The flow of data packets that are transmitted to, from, and within the website.
- Traffic rules: Network protocols that manage and control the flow of data.
- Public facilities and amenities: Applications and services on the website that fulfill particular functions for users.
Now, let’s delve into the various types of DDoS attacks.
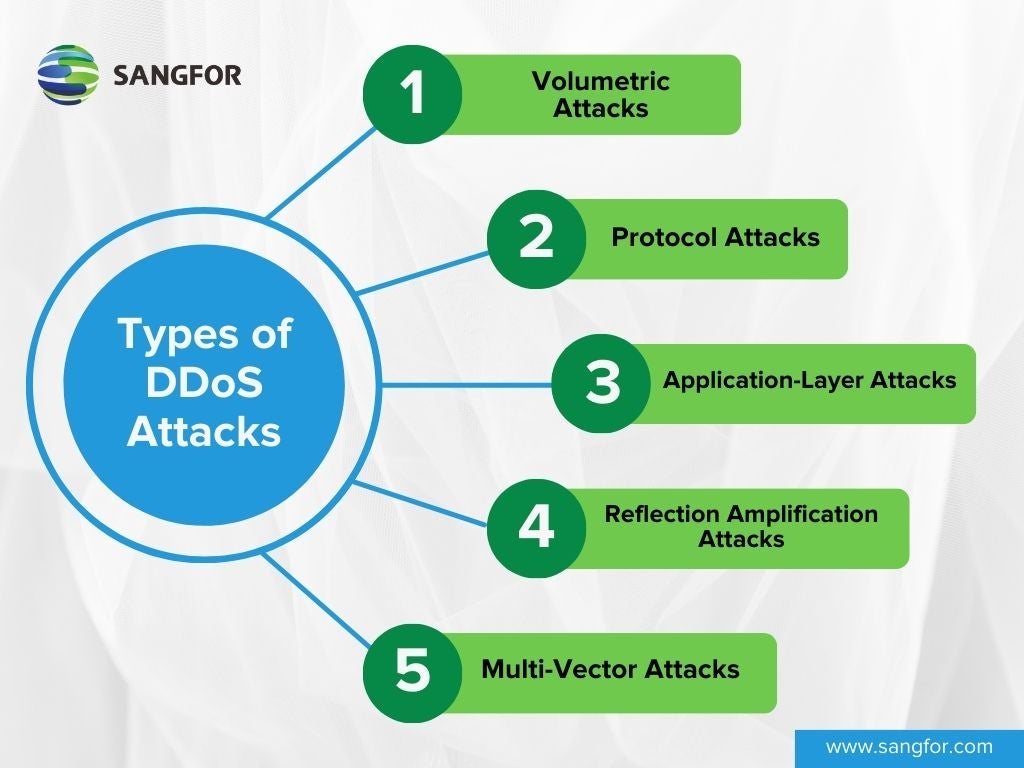
1. Volumetric Attacks
Volumetric attacks aim to overwhelm a target with a massive amount of traffic. Denial of service is achieved by saturating the target’s bandwidth so it can’t process new requests. Because volumetric attacks operate at the network layer (L3), which is responsible for packet forwarding, they are also known as network-layer DDoS attacks. The size of attacks is, therefore, measured in traffic volume, typically Gbps or Tbps. Due to their simplicity, volumetric attacks are the most common type of DDoS attack.
Analogy: In our city analogy, think of a volumetric DDoS attack as a massive influx of bogus road traffic (malicious requests) entering the city. The roads (network pathways) leading into the city are clogged with cars (data), blocking ordinary people (legitimate users) from accessing the city (the website).
Examples: UDP floods and ICMP (Ping) floods.
2. Protocol Attacks
Protocol attacks exploit weaknesses in the network or transport layer (L3/L4) protocols to disrupt the flow of data. The idea is to manipulate connections in a way that they occupy and exhaust the target’s infrastructure resources, preventing it from processing additional requests. Because protocol attacks also target L3 protocols like ICMP, they are also included in network-layer DDoS attacks and measured in Gbps or Tbps. Though not reliant on massive traffic volume, they still need significant traffic to succeed.
Analogy: These attacks are akin to breaking traffic rules (network protocols). This could be rogue drivers parking in the middle of an intersection (similar to a SYN flood attack) or a large truck ignoring an overpass height restriction to block the road (similar to a Ping of Death attack). This causes chaos and congestion, preventing people from accessing the city (the website) or its facilities (applications and services).
Examples: SYN floods, fragmented packet attacks, Ping of Death, and Smurf attacks.
3. Application-Layer Attacks
As the name suggests, these attacks target the application layer (L7) of computer systems, which are the applications or services of a website. The aim is to crash the web server through excessive HTTP requests, application calls, and transactions. Since application-layer DDoS attacks flood targets with requests rather than traffic volume, they are measured in requests per second (RPS).
Analogy: This is like overloading and causing disruptions at the city’s facilities themselves, like key transit hubs and hospitals. People are still able to reach these facilities (i.e., they can still access the website), but they aren’t able to receive any service (e.g., use an application on the website).
Examples: HTTP flood attacks, slowloris, and zero-day DDoS attacks.
4. Reflection Amplification Attacks
In reflection amplification attacks, attack traffic is amplified via an intermediary and redirected at the target to overwhelm it. This involves making small requests to a third-party server that returns a much larger response, such as a DNS server. The source of the requests is spoofed as the target’s address so that a huge volume of traffic is redirected to the target. Due to the nature of reflection amplification attacks, a relatively smaller botnet making fewer requests can reach or surpass the force of a larger botnet.
Analogy: Imagine if an attacker requested another city to send over a massive amount of transportation to the target city, say, for evacuation purposes. The sudden influx of transport arriving in the city would lead to extreme congestion. By making a small request, a significantly amplified response is provoked.
Examples: DNS amplification, NTP amplification, and SSDP amplification attacks.
5. Multi-Vector Attacks
These attacks combine two or more of the above methods to create a more complex attack that is harder to mitigate. The combination can involve different layers, like volumetric and application-layer attacks.
Famous Examples of DDoS Attacks
Some of the most famous DDoS attacks in history are notable either for their massive scale, the sophistication of the techniques used, or their significant impact on the targeted entities and the broader internet community. Here are a few of these notable attacks.
- Google Cloud DDoS Attack in 2022: The largest DDoS attack in 2022 occurred in June and was directed at a Google Cloud customer. This attack reached a peak of 46 million requests per second (RPS), making it the largest DDoS attack recorded that year. The attack began with over 10,000 RPS targeting the customer’s HTTP(S) load balancers and rapidly escalated to 100,000 RPS within eight minutes, eventually peaking at 46 million RPS.
- AWS DDoS Attack in 2020: Amazon Web Services (AWS) faced a gigantic DDoS attack in February 2020, which targeted an unidentified AWS customer. This attack used a technique called Connectionless Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (CLDAP) Reflection, which amplified the traffic sent to the victim’s IP address by 56 to 70 times. The attack peaked at an astonishing 2.3 Tbps and lasted for three days.
- Google DDoS Attack in 2020: Google experienced a record-breaking UDP amplification attack in 2020, sourced out of several Chinese ISPs. The attack on thousands of Google’s IP addresses lasted for six months and peaked at a staggering 2.5 Tbps. This remains the largest bandwidth attack known as of the time of reporting.
- GitHub DDoS Attack in 2018: On February 28, 2018, GitHub was hit with a DDoS attack that clocked in at 1.35 Tbps and lasted for about 20 minutes. This attack was notable for exploiting the Memcached database caching system, providing an amplification factor of up to 51,200 times.
- Mirai Dyn DDoS Attack in 2016: On October 21, 2016, Dyn, a major Domain Name Service provider, was hit by a traffic flood of 1 Tbps, becoming the new record for a DDoS attack at the time. This attack, also attributed to the Mirai botnet, impacted high-profile websites like GitHub, HBO, Twitter, Reddit, PayPal, Netflix, and Airbnb.
- Mirai Krebs and OVH DDoS Attacks in 2016: On September 20, 2016, the blog of cybersecurity expert Brian Krebs was hit by a DDoS attack in excess of 620 Gbps, which was the largest attack seen at the time. The Mirai botnet, which was responsible for this attack, later targeted OVH, one of Europe’s largest hosting providers. This attack on an OVH customer was driven by an estimated 145,000 bots, generating a traffic load of up to 1.1 Tbps and lasted about seven days.
Motives of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks are launched for a wide variety of reasons, all with malicious intent. The main motives behind DDoS attacks include:
- Financial Gain: Attackers often target businesses for financial extortion, demanding payment to stop the attack. This often occurs in triple extortion ransomware attacks, where victims are subjected to DDoS attacks in addition to data theft and encryption to put more pressure on them to pay.
- Business Competition: Companies might use DDoS attacks to disrupt the operations of competitors and gain a competitive advantage. This is often achieved by hiring third-party attackers offering DDoS as a Service, often marketed as “Booter” or “Stresser” services.
- Hacktivism: Hacktivists use DDoS attacks as a form of protest against governments, organizations, or individuals whose policies or actions they oppose.
- Personal Vendettas: Individuals might launch DDoS attacks as a means of revenge against an organization. Again, these attacks are enabled by DDoS services, with prices low enough to be within the reach of individuals. Some services even offer short attacks for as little as a few dollars.
- Diversion Tactics: A DDoS attack can be a smokescreen for other malicious activities like data breaches. While the victim is focused on mitigating the DDoS attack, attackers use the opportunity to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive data.
The wide range of motivations and the availability of DDoS as a Service means that almost any business or individual can be the target of a DDoS attack.
DDoS Attack Statistics and Trends
The Cloudflare DDoS threat report for Q3 2023 provides comprehensive insights into DDoS attacks. Cloudflare’s extensive network infrastructure and position as a key intermediary for internet traffic make it well-qualified to provide reliable statistics on DDoS attacks.
DDoS Attack Volume:
Application-layer (HTTP) DDoS Attacks:
- 8.9 trillion attack requests in 3Q2023, a 65% increase from the previous quarter.
- 19 trillion attack requests between 1Q2023 and 3Q2023.
Network-layer (L3/L4) DDoS Attacks:
- 2.1 million attacks in 3Q2023, a 14% increase from the previous quarter.
- 6 million attacks between 1Q2023 and 3Q2023.
Hyper-Volumetric Attacks:
- Cloudflare mitigated thousands of hyper-volumetric HTTP DDoS attacks in 3Q2023. The average attack rate was 30 million requests per second (RPS), with 89 attacks exceeding 100 million RPS. The largest attack peaked at 201 million RPS, which was three times larger than the previous record.
- These hyper-volumetric attacks leverage the HTTP/2 Rapid Reset vulnerability (CVE-2023-44487), which has been exploited since August 2023.
- These attacks often utilize virtual machine (VM) based botnets, which can deliver up to 5000 times impact per node compared to traditional IoT botnets.
Targeted Industries:
Application-layer (HTTP) DDoS Attacks:
- Top 3 targeted industries by absolute attack traffic volume: Gaming and Gambling (5.41%), Information Technology and Internet (4.38%), and Cryptocurrency (3.43%).
- Top 3 targeted industries by attack traffic relative to own traffic: Mining and Metals (17.46%), Non-Profits (17.41%), and Pharmaceuticals, Biotechnology, and Health (14.77%).
- Regional focus: Computer Software industry in North America, Gaming and Gambling in Europe, Cryptocurrency in Asia, Retail in the Middle East, etc.
Network-layer (L3/L4) DDoS Attacks:
- Top 3 targeted industries by absolute attack traffic volume: Information Technology and Internet (34.86%), Telecommunications (3.01%), and Gambling and Gaming (1.51%).
- Top 3 targeted industries by attack traffic relative to own traffic: Music (21.3%), Computer and Network Security (21.3%), and Information Technology and Internet (16.1%).
Targeted Countries:
Application-layer (HTTP) DDoS Attacks:
- Top 3 targeted countries by absolute attack traffic volume: US (4.867%), Singapore (3.120%), and China (2.208%).
- Top 3 targeted countries by attack traffic relative to own traffic: Anguilla (75.51%), American Samoa (21.60%), and British Virgin Islands (12.83%).
Network-layer (L3/L4) DDoS Attacks:
- Top 3 targeted countries by absolute attack traffic volume: China (29.22%), US (3.55%), and Taiwan (2.97%).
- Top 3 targeted countries by attack traffic relative to own traffic: China (73.0%), Netherlands (35.0%), and Thailand (30.0%).
Source of Attack Traffic:
Application-layer (HTTP) DDoS Attacks:
- Top 3 sources by absolute attack traffic volume: US (15.78%), China (12.62%), and Brazil (8.74%).
- Top 3 sources by attack traffic relative to own traffic: Mozambique (21.4%), Egypt (13.4%), and Libya (12.9%).
Network-layer (L3/L4) DDoS Attacks:
- Top 3 sources by absolute attack traffic volume: US (36.6%), Germany (7.9%), and the UK (4.7%).
- Top 3 sources by attack traffic relative to own traffic: New Caledonia (39.12%), Vietnam (38.14%), and Paraguay (30.77%).
Attack Vectors:
- Top attack vectors: DNS floods (46.74%), SYN floods (22.08%), followed by RST floods (6.16%), UDP floods (5.29%), and Mirai botnet attacks (3.58%).
- Emerging trends in DDoS attack strategies include a significant increase in mDNS (multicast DNS) attacks (456%), CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) attacks (387%), and ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) DDoS attacks (303%).
- Ransom DDoS attacks decreased for the second successive quarter (from 12% to 8%).
Why DDoS Attacks are Difficult to Prevent
The DDoS attack examples, statistics, and trends discussed in this article underscore the growing prevalence, sophistication, and effectiveness of DDoS attacks. What drives this trend? Below, we explore several factors that make DDoS attacks difficult to detect and mitigate.
- Mimicking Legitimate Traffic: Particularly in application-layer attacks, the traffic generated can closely mimic legitimate user traffic, making it difficult to distinguish between normal and malicious requests.
- Distributed Nature of Attacks: DDoS attacks often originate from a large number of compromised devices (bots), which can be geographically dispersed. This widespread nature makes the traffic appear more like regular, distributed internet traffic rather than a coordinated attack.
- IP Spoofing: The use of spoofed IP addresses in DDoS attacks can mask the true origin of the attack traffic, adding another layer of complexity to traffic analysis.
- Dynamic and Evolving Attack Patterns: Attackers frequently change attack vectors and patterns to evade detection. They may vary packet sizes, switch between target services, or alter traffic behavior, making consistent detection challenging.
- Volume and Scale of Traffic: The sheer volume of traffic in a large-scale DDoS attack can overwhelm not just the target but also the monitoring and detection systems, hampering effective analysis.
- Use of Low and Slow Attack Techniques: Some sophisticated DDoS attacks use low-and-slow techniques, generating traffic that doesn’t significantly deviate from normal bandwidth but targets specific vulnerabilities or components of a service, making detection more complex.
How to Prevent and Stop DDoS Attacks
As discussed above, DDoS attacks can be very challenging to detect and stop. Therefore, no single method of protection is foolproof. A combination of techniques is required to effectively prevent, detect, and mitigate DDoS attacks. Here are seven common strategies to protect against DDoS attacks, along with their respective shortcomings.
Network Redundancy
This involves setting up redundant network resources like servers and bandwidth to handle excess traffic. By distributing the load across multiple servers and data centers, the impact of a DDoS attack can be mitigated.
Shortcomings: The cost of maintaining redundant systems can be high. Moreover, if the attack is large enough, it can still overwhelm these redundant resources.
Rate Limiting
Rate limiting controls the amount of traffic that is allowed to a network or a server. This helps in preventing the server from becoming overwhelmed by too many requests at once.
Shortcomings: Legitimate traffic may also be blocked or limited if the rate limiting is too aggressive. It requires fine-tuning to balance between normal traffic flow and DDoS protection.
Blackhole Routing
This technique routes all traffic to a “black hole” to protect the target server or network during a DDoS attack. Malicious traffic is typically diverted to a null route or IP address where it can do no harm.
Shortcomings: Blackhole routing is a drastic measure as it not only blocks malicious traffic but also legitimate traffic. This results in service downtime for normal users. It’s more of a temporary and emergency measure rather than a long-term solution.
Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
A WAF protects web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet. They use a set of rules to distinguish between legitimate and malicious requests.
Shortcomings: WAFs need regular updates to protect against new types of attacks and can sometimes block legitimate traffic, resulting in false positives. This problem can be mitigated by using AI-based semantic analysis, which continuously learns attack patterns to recognize unknown threats.
Anomaly-Based Detection
This approach involves analyzing traffic patterns and using machine learning algorithms to detect and mitigate unusual or malicious traffic patterns typical of DDoS attacks.
Shortcomings: Requires a significant amount of data to train the algorithms effectively. False positives can occur, leading to legitimate traffic being blocked. It may also be less effective against newly emerging attack vectors that haven’t been previously encountered.
Anycast Network Diffusion
In an anycast network, a single IP address is shared among multiple servers located in different geographical locations. When a DDoS attack occurs, traffic is spread across these servers, diluting the impact.
Shortcomings: Anycast can be less effective for non-volumetric attacks like application-layer attacks and requires a sophisticated routing infrastructure.
Cloud-Based Protection Services
These services offer large-scale defense infrastructure that can absorb high volumes of traffic. They typically combine several DDoS mitigation techniques, like rate limiting, WAFs, and traffic analysis.
Shortcomings: Such services may be costly and may not be suitable for all businesses, especially smaller ones with limited budgets. Additionally, relying on external services means trusting a third-party provider with critical aspects of your network security.
Learn more with Sangfor
To learn more about distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks and how to protect your business or organization from them, don’t hesitate to get in touch with a specialist from Sangfor.





