In the early days of the internet, passwords became a common form of authentication. At this point in time, simple passwords like your mother’s maiden name or your dog’s nickname were more than enough to keep your account secure. But as the internet progressed and more of our lives began to depend on and take place in the digital space, security threats became more prevalent.
Nowadays, online platforms often impose requirements on password strength and make you include capital letters, numbers, or special characters. But given that modern hackers are equipped with a myriad of ways to crack even gibberish passwords, another layer of defense is necessary. This is where two step authentication comes into play. Read this article to learn exactly what two step authentication is, how it works, and much more.
What is two step authentication?

Two step authentication, also known as 2SA, is a security mechanism designed to verify a user’s identity using two separate steps. In two step authentication, the user is prompted to enter information that verifies their identity. This is considered the first step and is normally some form of account credentials like your username and password.
If the user can validate their identity in the first step, they are immediately asked to enter another piece of information to re-confirm their identity. This can be one of several pieces of information such as a memorable answer or something else only the user should know.
If the user completes both steps of the verification successfully, they are granted authorization to access the account. Two step authentication is considered much more secure than a regular one-step system as it requires the knowledge of two distinct pieces of information. For hackers trying to gain access, this multiplies the difficulty significantly.
What is the difference between two step authentication and two-factor authentication?
Two step authentication and two factor authentication (2FA) are often incorrectly used interchangeably. While the two verification systems are very similar in nature and purpose, there is a distinct difference between them.
As discussed, two step authentication requires the user to pass two verification steps to be granted authorization. Two-factor authentication asks the same of the user but will not use the same authentication factor twice. Learn more about authentication factors below.
Understanding the different authentication factors
Knowledge
The knowledge factor is something that you know. Usually, knowledge factors are things like passwords or pin numbers that you have made up and kept secret to yourself. Some one-time pins are also considered as the knowledge factor as they can be received on the same device accessing the account.
Possession
The possession factor encompasses something that you have. Common examples of the possession authentication factor include authentication apps on your smartphone, SMS one-time pins, and physical security devices.
Biometrics
The biometric authentication factor is something which you are. It might be easy for hackers to crack passwords nowadays, but your fingerprint or facial ID is highly secure.
How are the authentication factors used in 2FA and 2SA?
Two step authentication almost always uses the knowledge factor twice. For example, some accounts are protected by a password and a memorable answer. Both of these are something that you know. Technically speaking, it could use either of the other two twice as well - although this is less common.
Two-factor authentication takes this to another level by utilizing two of the above three factors. For example, two-factor authentication may require a password (knowledge factor) before a one-time code is sent to your phone (possession factor).
What is the more secure option?
Two-factor authentication is a more secure option than two step authentication, as it requires more than one authentication factor.
Think of using several authentication factors as spreading components of a key across the world. The hacker cannot simply find all the parts in one place, put them together, and use the key. They must travel across continents to find what they need. More often than not, this acts as an effective deterrent for hackers. The account is simply not worth the effort for them when there are many less protected accounts.
What about multi-factor authentication?
Multi-factor authentication takes this to another level, as with each added authentication factor layer, the account is better protected. Multi-factor authentication works under the exact same principles as two-step or two-factor authentication. The difference is that multi-factor authentication uses two or more factors and as many steps. In this sense, multi-factor authentication is an even more secure option for accounts that need the utmost protection. For most consumer accounts, multi-factor authentication is considered unnecessary.
How does two step authentication work?
There are several different methods of completing two step authentication, depending on the platform. Businesses use their own variety of two-step or two-factor authentication to improve the security of their services. After all, their reputation as a reliable service provider depends on their ability to keep users’ accounts secure.
Logging into your Google, iCloud, or other online account looks like this:
Part #1: The user is prompted with the login screen. Here, they enter their username and password.
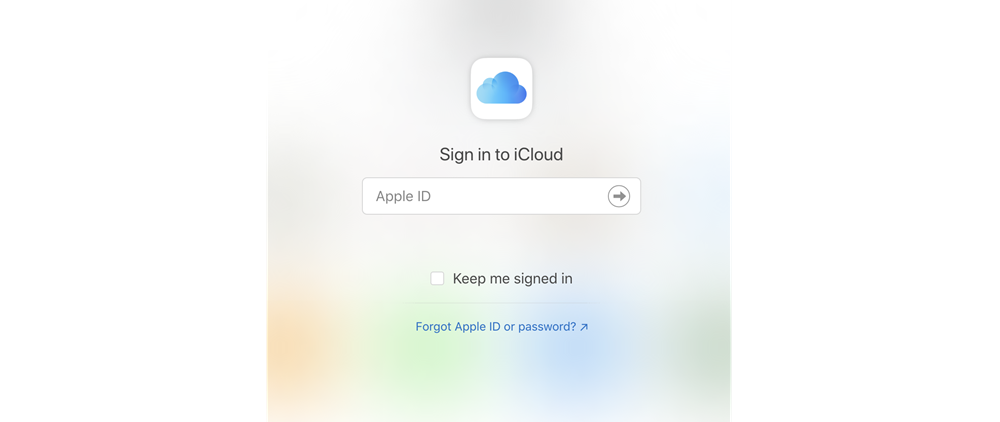
Part #2: If they enter their account credentials correctly, they will be prompted with another screen asking for the second step.
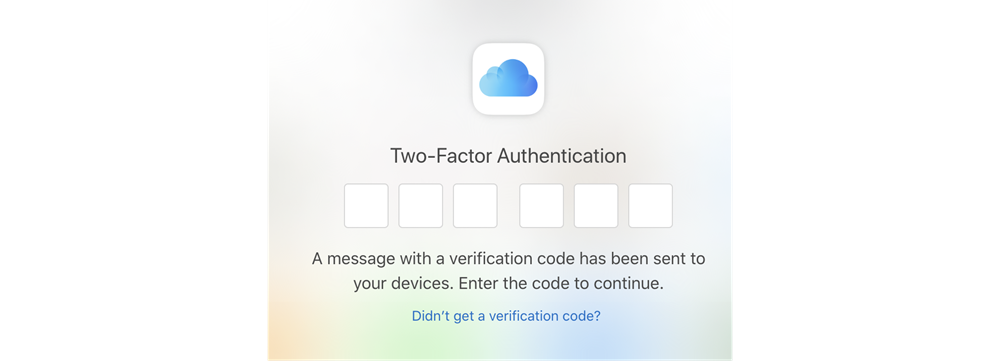
Part #3: If the user enters the information correctly, they are granted access to the account.
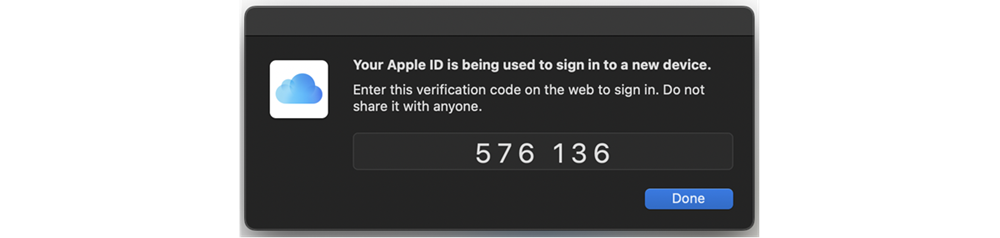
Safety nets for authentication loss
Businesses that run online services using two-factor or two step authentication understand that an authentication method can be lost. Fortunately, any reliable provider has protective measures in place to mitigate such an event.
Losing your password or phone:
In the event of losing a password, all major providers like Google have an easy and straightforward way for the legitimate account owner to bypass two step authentication using alternate authentication methods. These methods are designed to be just as secure, albeit less convenient than the usual method. For example:
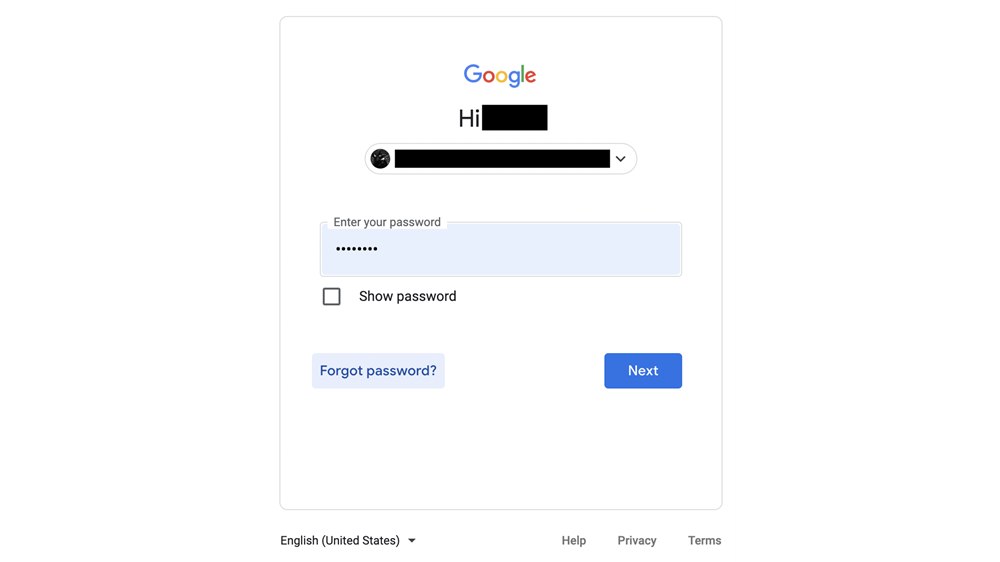
Clicking "Forgot password?" on the above screen takes you here:
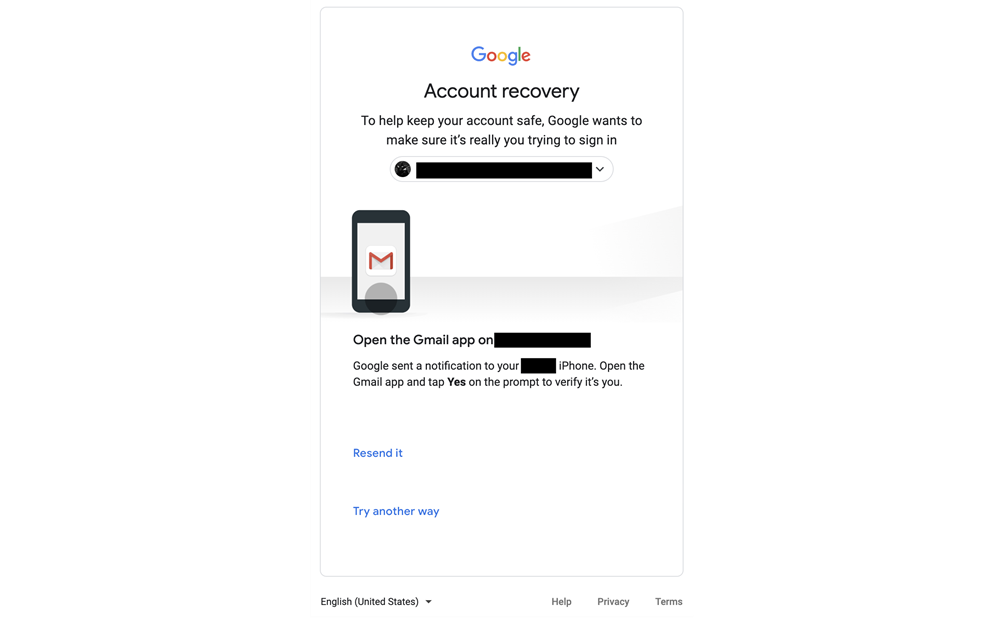
Following the on-screen instructions, the user is prompted to open the Gmail app on their phone and tap Yes to verify their identity through the possession authentication factor. However, if the user does not have their phone at the ready (or even if they have lost it), there is another method:
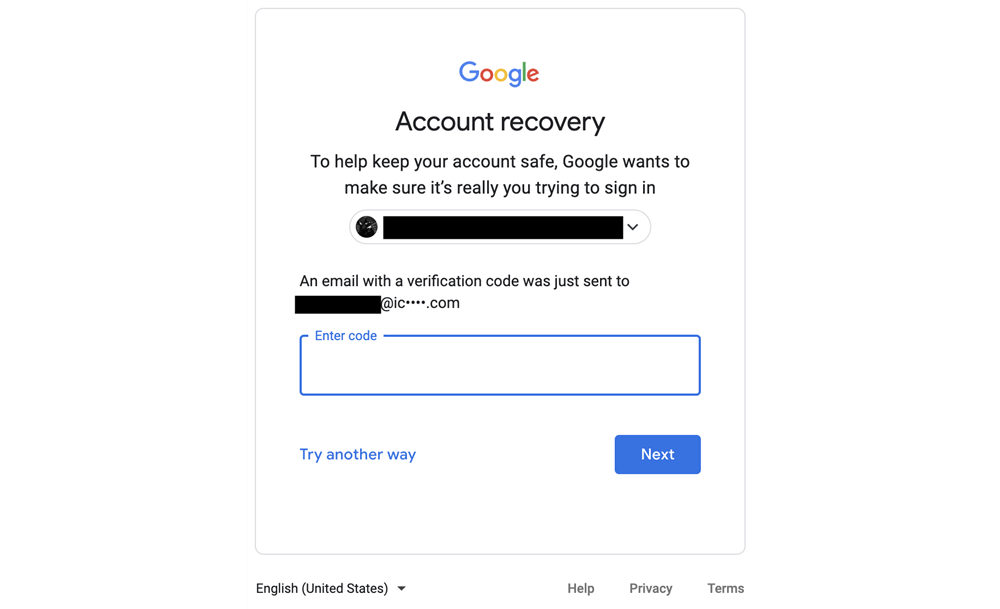
When creating your Google account, you will have been prompted to add a backup email. This email is used to receive a verification code that will unlock your account. Using a backup email like this, especially with another reliable provider, your account remains secure. This is because the backup account should also be protected by two-step or two-factor authentication separately.
Note: all major providers will have their own methods of recovering an account. While the steps may vary, the ultimate emphasis on all of these recovery methods is to only restore the account to the rightful owner.
Why should I use two-factor or two step authentication?
Keyloggers, brute-force attacks, phishing, and many other methods of stealing passwords are very real threats. Accounts protected with only a password as a single layer of authentication are always at risk.
Two-step authentication is an effective way for you to protect your accounts for several reasons:
The pros of two step authentication
Increases the security of your accounts or applications
Accounts not protected by an additional layer of defense are sitting ducks for hackers. Using 2SA or 2FA will keep your personal information and accounts safe. This is even more important for businesses or agencies that have sensitive client information. Protecting users’ accounts means protecting your business’ reputation.
Convenient in use
Most accounts when used on the same device will not require you to log in each time. When you do decide to log in from a new device, two step authentication is quick and easy, given you are the account holder.
However, no security measure is without flaws. Two step authentication proves highly valuable to many users, but has some limitations that you should be aware of:
The cons of two step authentication
Single-factor two step authentication is not as safe as two-factor authentication
Two step authentication by nature only uses one authentication factor. Two-factor authentication is the more secure option and should be used where possible in favor of single-factor two step authentication.
Cyber criminals are always finding new ways of hacking accounts
While both two-step and two-factor authentication can help secure your account in the vast majority of cases, they are not perfect. Hackers are finding new and ingenious ways of bypassing these security measures. This is done either by deactivating them or through social engineering tactics like phishing attacks.
Protect your organization with Sangfor
The only way to properly protect your personal and business in the digital age is to use layered security architecture. This means next-gen firewalls, endpoint security, and more alongside 2FA and 2SA.
Get in touch with Sangfor today to learn more about our leading cyber security solutions.





