The Worldwide Web is a wonderful place, full of opportunities and possibilities. Ever since its inception in the 1980s, the Internet has continued to expand at an incredible rate. With advancements constantly being made across the board, the Internet is used in just about every sphere of life. Today, it has become an inseparable part of both business and leisure. Unfortunately, along with the opportunities provided by the Internet comes the potential for malevolent activity too. As the web continues to expand and become increasingly complex, the number of ways in which hackers can cause trouble grows. Most people are familiar with computer viruses, but the broader notion of Malware encompasses far more than many realize. Without fully understanding what Malware is, its definition, meaning, and how it works, there’s no way one would be able to protect themselves and their businesses against potential threats.
This article will step into the world of Malware, providing its definition, meaning, and how it works. You’ll learn what Malware is, how it works, and you can defend against them using anti-Malware solutions, Malware scans, and Malware removal techniques.
What is Malware?

Malware, otherwise referred to as Malware, is a broad term encompassing any kind of software that intends to harm the user in some form.
There are several common motivators for hackers to use Malware as a weapon against individuals or organizations. Here are a few:
Financial incentive
Hackers may use Malware to procure financial rewards from their targets. This is most relevant with high-profile victims like big organizations. Some examples are Ransomware attacks in Colonial Pipeline, JBS Ransomware attack, or more recently, the conti ransomware attack in Cost Rica.
Hacktivism
Generally, hacktivists target large organizations in the public eye to humiliate them or send a message to them and the public. They use Malware to break into sophisticated security systems. The motivations behind this may be social or political.
Revenge
Often, hackers use Malware to implement revenge plots against individuals or organizations they believe have done them wrong. In this case, the attack is purely motivated by anger, often without fear of repercussion.
Infamy
For some, it’s as simple as gaining recognition for their activity and expertise. These days, in a world ruled by social media, it is far easier for one to gain recognition on a global scale. Using Malware is one way to do it.
Challenge
For some hackers, it’s simply about a challenge: to break an “unbreakable” system. While one may hope that IT and software specialists will use their expertise for good, sometimes it is malevolent activity that attracts them.
Subversion
Subversion is the act of using Malware as a tool in corporate espionage to meddle in corporate and social affairs and sabotage large projects and organizations.
There are several motivators behind using Malware against an individual or organization. However, the intention to cause harm to gain unauthorized access to data or applications is universal amongst them. Furthermore, these acts are often carried out with no regard for the harm it will cause the victim.
In a world in which Malware and hacking run rife, ensuring that you or your organization have top-tier cybersecurity is essential.
How does Malware work?
One of the most important things to know about Malware is that it is not limited to computers. In fact, any device that can connect to the Internet is vulnerable to being infected by Malware. That means your business enterprises are at a higher risk of Malware intrusion.
There are many different things that hackers may do once a device is infected. Here is a rundown of the most common:
Taking control
Once a hacker has infected your device, they may be able to take complete control of it. This can include changing and resetting passwords, installing programs, and even stealing intellectual property. Essentially, anything that is on your device that has been infected is accessible to the hacker.
Ransomware attacks
Ransomware attacks generally target large corporations and organizations with large amounts of money at stake. Ransomware attacks aim to gain access to computer systems and devices through phishing or other socially engineered plots, and they go on to infect your device with Malware.
After encrypting a hard drive, they demand a large sum of money in exchange for regaining access to their own system and/or data. In theory, once the amount is paid, the hackers remove the encryption. However, there is no guarantee.
Keyloggers
As mentioned, ransomware attacks tend to target large organizations rather than individuals. When it comes to exploiting individuals financially, hackers tend to use keylogging.
Infecting an individual’s device with Malware that allows them to see, follow, and record all their activity. This constitutes a massive invasion of privacy but the biggest risk is their ability to gain access to sensitive information like credit card details, online banking login details, and more.
Although keylogging attacks are typically on a much smaller scale than ransomware, they are just as serious for the individual.
APT Malware
Hackers often use Malware for personal reasons. For example, they may be carrying out vendettas against organizations or individuals who they believe have done them wrong.
In the case of APT Malware, it’s more about individuals targeting other individuals familiar to them. This may be a spouse, a former partner, or any other kind of acquaintance. In cases such as this, APT Malware (advanced persistent threat Malware) may be used to gather information about the target without being detected.
Essentially, APT Malware allows hackers to gain access to systems and lurk undetected in the background of them. In doing so, they can gather information about their targets without drawing attention to themselves.
While it may seem relatively benign, the use of APT Malware against individuals is often incredibly sinister and a cause for alarm. Hackers can use information gained by this method to find out personal information about individuals that may leave them vulnerable. In fact, in the most extreme cases, APT Malware has been used by malicious personalities – such as stalkers and even murder by serial killers – to track down their targets and do them harm.
Trojans
Trojans portray themselves as trusted programs to gain access to a device. Unsuspecting individuals download a trojan thinking that it is, in fact, reputable and safe software. However, in reality, they act as vectors that enable harmful Malware to be installed.
The lesson here is to never be too trusting when it comes to downloading foreign programs and software!
Password crackers
Password crackers are programs that work to figure out your passwords. As a form of Malware, these programs gain access to your device and work through hundreds and thousands of possible passwords to guess your password through brute force.
Fortunately, running a password cracker is a very time-consuming process. Furthermore, the longer and more complex your password, the more options there are statistically. In turn, this means it will take far long for the password cracker to guess your password. This gives you and your cybersecurity software more time to detect and eliminate the Malware.
Worms
Worms are one of the most harmful types of computer viruses in circulation and can cause widespread damage. Unlike other forms of Malware, worms are not only able to infect systems and devices but will subsequently self-replicate and spread to any other devices and systems that they encounter. Because of this, worms have far-reaching consequences and have the potential to cause major damage in a short amount of time.
[Webinar] Malware Evasion: Why It Works
To gain deeper insights into how malware evades detection and why traditional security measures sometimes fail, we recommend watching this informative webinar:
How to protect yourself or your organization from Malware
Clearly, Malware can be incredibly harmful to your personal devices. Given that it’s always preferable to entirely prevent a security incident than deal with the ramifications afterwards, here are a few ways you can try and get ahead of potential hackers.
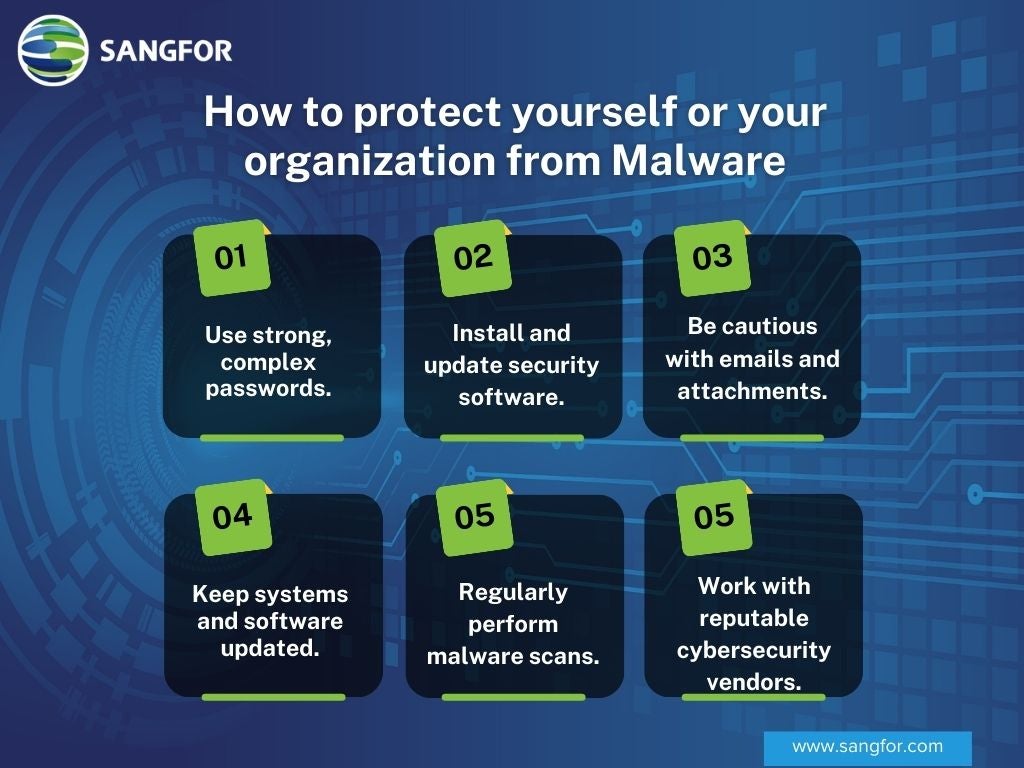
Always use strong passwords
The stronger your password, the higher chance you have of avoiding being hacked. But what constitutes a strong password?
There are a few aspects of passwords that are important. To create a strong password:
- It needs to be between 18 and 20 characters long
- It must contain at least one number or symbol
- It can’t contain dictionary words
- It must be made up of both upper- and lower-case letters
The best thing you could possibly do is make up a password that is complete nonsense. That way, the chances of your password being figured out are far lower. Just make sure you can remember it!
Install Reliable Security Software
Using reputable security software and anti-malware programs is essential for detecting and removing malware. These programs provide real-time protection against malicious programs, infected files, and other threats. Regularly update your software to ensure it can protect against the latest threats.
Digital disguises
For Malware to be able to function effectively, they need to be designed for a specific operating system such as Windows, Apple or Linux. If the Malware that infects your device is suited to a different operating system than what you are using, it won’t be effective.
Thus, it’s possible to use this against hackers. By disguising your operating system, you are able to confuse and deter hackers.
Be careful of where you click
Phishing is one of the most common sources of hacking and viruses as it’s not always easy to detect scams. Pay extra attention not to click on booby-trapped links or download malicious email attachments. These are links embedded with malware that will infect your device once you click them.
There is no easy way to prevent this. The best way is to simply take special care when receiving emails from unknown senders and train your staff on some of the key pointers of phishing emails.
Hack Use a Malware Scanner
Regularly scanning your devices with a malware scanner helps detect and remove any malware that may have infiltrated your system. Schedule regular malware scans to ensure your devices remain clean.
Stay updated
Hackers and software developers are constantly trying to outsmart each other, coming up with innovative ways to hack into systems and sophisticated ways in which to fool hackers respectively.
As the saying goes, prevention is better than cure. Therefore, one of the best things you can do to protect yourself from malicious activity is to ensure that your devices are always up to date. Computer systems are constantly tweaked and changed to ensure they offer the best protection possible to you and your data from known Malware. In short, the more updated your device is, the safer you will be.
Work with a reputable cyber security solutions vendor
One of the best ways to protect against cyber security threats is through a layered architecture of cyber security solutions. Software such as a next-generation firewall like Sangfor NGAF, endpoint security, cloud-based SASE, and other cyber security solutions can lock down your cloud premises from Malware. Each business will have a different set of needs and requirements, so be sure to talk to a specialist to find out exactly what is necessary.
Read more about 10 ways you can improve your network security and continue smooth, uninterrupted business growth.
Final thoughts on Malware
While the Internet brings with it boundless opportunity and endless potential for innovation and development, it also introduces the potential for danger and malevolent activity. While not all kinds of hacking and Malware may be prevented from causing damage, technological advancements allow users to have a better shot at protecting themselves.
Learn more about some of the cyber security solutions to protect from ransomware and Malware offered at Sangfor and how you can protect your business from the dangers of Malware. For any additional questions, do not hesitate to get in touch with one of our specialists.
Frequently Asked Questions About Malware
What is Malware?
Malware is a broad term encompassing any kind of software that intends to harm the user in some form.
What is the difference between a virus and malware?
Malware is a broad term that refers to any malicious software designed to harm or exploit any programmable device or network. A virus is a specific type of malware that replicates by attaching itself to clean files and spreading to other files.
How can I tell if my computer is infected with malware?
Common signs include slow performance, frequent crashes, unexpected pop-up ads, unfamiliar programs starting automatically, and excessive hard drive activity. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's advisable to run a malware scan.
Can mobile devices get infected with malware?
Yes, smartphones and tablets are also vulnerable to malware attacks. It's important to download apps only from trusted sources, keep your operating system updated, and use security software designed for mobile devices.
Is antivirus software enough to protect against all types of malware?
While antivirus software is essential, it may not protect against all types of malware, especially new or sophisticated threats. Combining antivirus software with other security measures like firewalls, anti-malware programs, and safe browsing practices offers better protection.
What should I do if my system is infected with ransomware?
Disconnect your device from the network immediately to prevent the malware from spreading. Do not pay the ransom, as there's no guarantee your data will be restored. Contact cybersecurity professionals who can help you remove the malware and possibly recover your data.
How does malware spread?
Malware can spread through malicious email attachments, infected software downloads, compromised websites, and even through web browser vulnerabilities. Social engineering tactics like phishing are commonly used to trick users into downloading malware.
Can malware affect my business even if we have security measures in place?
Yes, no security measure is foolproof. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and attackers often find new vulnerabilities to exploit. Regularly updating your security protocols and educating employees about cybersecurity best practices can help mitigate risks.
What is a zero-day vulnerability?
A zero-day vulnerability is a software flaw that is unknown to the software vendor and has no patch or fix available. Attackers exploit these vulnerabilities to deliver malware before developers can address the issue.
How often should I update my security software?
You should enable automatic updates for your security software to ensure it has the latest threat definitions. Regular updates are crucial for protecting against new and emerging malware threats.
Is it safe to use public Wi-Fi networks?
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making it easier for attackers to intercept your data or deliver malware. If you must use public Wi-Fi, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your connection.





